ServiceNow Security Assessment Checklist
Download seven ServiceNow security controls checklist designed to protect data, reduce exposure, and support a stronger security posture.
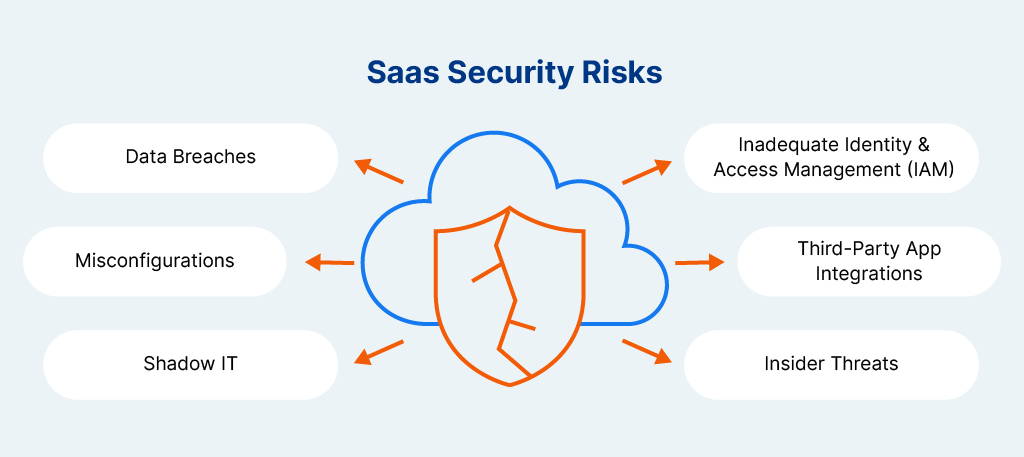
SaaS security risks refer to the potential threats and vulnerabilities that arise when organizations use cloud-based applications to store, manage, and transmit data. Because SaaS platforms are hosted and maintained by third-party vendors, businesses often have less visibility and control over how data is protected.
Common risks include unauthorized access, misconfigurations, data breaches, and third-party integrations that expose sensitive information. As SaaS adoption continues to grow, so does the importance of understanding and mitigating these security challenges to protect company and customer data.
While SaaS platforms offer scalability and convenience, they also introduce a unique set of security challenges. Some of the most significant risks in a SaaS model include:
Because SaaS applications often store sensitive business and customer data in the cloud, they are prime targets for cyberattacks. A breach can result in data loss, financial damage, and reputational harm.
Misconfigured access controls, sharing settings, or integrations can unintentionally expose critical data. This is one of the most common causes of SaaS-related vulnerabilities, often due to user error or lack of security oversight.
Employees may adopt unauthorized SaaS tools without IT’s knowledge, creating blind spots in the organization’s security posture. These unsanctioned apps often lack proper vetting and can bypass established security protocols.
Weak or improperly managed IAM practices can lead to unauthorized access to SaaS applications. This includes poor password hygiene, lack of MFA, or failure to deprovision accounts when employees leave.
Many SaaS platforms rely on integrations with other apps and APIs. These third-party connections can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly assessed and monitored, expanding the potential attack surface.
Whether intentional or accidental, employees and contractors with access to SaaS applications can pose a significant risk, especially if they misuse or mishandle sensitive data.
Addressing these risks requires a combination of strong security policies, visibility into app usage, continuous monitoring, and advanced SaaS security solutions tailored to today’s cloud-first environment.
Mitigating SaaS security risks requires a proactive, layered approach that combines technology, processes, and people. Here are key strategies organizations can implement to strengthen their SaaS security posture:
Implement Strong Identity and Access Controls. Use robust identity and access management (IAM) protocols to control who can access your SaaS applications. This includes enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and role-based access controls to minimize unnecessary privileges.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Risk Assessments. Routinely evaluate the security of your SaaS environment. This includes reviewing user permissions, app configurations, and third-party integrations to identify vulnerabilities before they’re exploited.
Monitor User Activity and Behavior. Continuous monitoring helps detect unusual or unauthorized activity in real-time. Behavioral analytics tools can flag anomalies, such as data exfiltration or suspicious login patterns, that may signal a breach.
Establish a SaaS Security Policy. Create clear internal guidelines for SaaS usage across departments. This policy should define approved apps, outline security responsibilities, and include processes for onboarding and offboarding users.
Secure Data Through Encryption. Ensure data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Additionally, understand the encryption practices of each SaaS provider to confirm they align with your organization’s compliance and security standards.
Vet Third-Party Apps and Vendors Carefully. Before integrating third-party tools, assess their security practices, compliance certifications (like SOC 2 or ISO 27001), and data handling policies. Limit integrations to those that meet your minimum security requirements.
Use a SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) Tool. SSPM platforms provide centralized visibility, automate misconfiguration detection, and help enforce consistent security controls across your SaaS stack, which greatly reduces risk and operational overhead.
By implementing these practices, organizations can gain better visibility, reduce exposure, and build a more resilient SaaS security framework that evolves alongside their technology stack.
A SaaS security risk assessment is a structured process that helps organizations identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks associated with their use of cloud-based applications. It’s a critical step in building a strong security foundation and ensuring compliance with data protection standards. Here’s what it typically includes:
Inventory of SaaS Applications. Start by identifying all SaaS applications in use across the organization, both approved and unapproved (shadow IT). Without full visibility, it’s impossible to assess risk accurately.
User Access and Permissions Review. Examine how users access each SaaS app and what permissions they have. Assess whether access is aligned with job roles and if practices like least-privilege access and multi-factor authentication are enforced.
Configuration and Settings Audit. Review the security settings and configurations of each platform. This includes data sharing settings, public link exposures, password policies, and admin privileges (areas where misconfigurations can introduce major vulnerabilities).
Third-Party Integrations Analysis. Map out which third-party tools are connected to your SaaS apps and evaluate the security of those integrations. Poorly vetted or excessive integrations can expand your attack surface significantly.
Data Sensitivity and Exposure Mapping. Determine what types of sensitive data (e.g., PII, financial records, IP) are stored or transmitted through SaaS platforms. Understand where data resides, who can access it, and whether it’s adequately protected.
Vendor Security Posture Evaluation. Assess the security practices of your SaaS vendors. Look for compliance certifications (like SOC 2, ISO 27001), data residency policies, breach notification procedures, and their approach to encryption and access control.
Monitoring and Logging Capabilities. Evaluate each application’s ability to generate logs and support monitoring. Strong logging and alerting capabilities are essential for detecting and responding to security incidents.
Risk Scoring and Prioritization. Once risks are identified, assign a risk score based on likelihood and impact. This helps prioritize remediation efforts and allocate resources efficiently.
Conducting a comprehensive SaaS security risk assessment not only helps uncover blind spots but also builds a roadmap for reducing vulnerabilities and improving governance over time.
Yes. AppOmni offers a comprehensive SaaS Risk Assessment designed to give organizations complete visibility into their SaaS environments, uncover hidden vulnerabilities, and prioritize areas of risk. With this assessment, security teams can evaluate how data is being accessed, shared, and exposed (both internally and externally) across critical SaaS platforms.
The assessment identifies misconfigurations, risky third-party integrations, and over-privileged users, helping teams address gaps before they become incidents. It’s fast, non-invasive, and delivers actionable insights that map directly to your business’s security posture.
AppOmni also offers a full suite of SaaS Security Solutions to extend beyond assessment. It enables continuous monitoring, automated policy enforcement, and real-time threat detection across your SaaS stack.
Whether you’re just starting your SaaS security journey or looking to strengthen an existing program, AppOmni helps you take control of your SaaS risk with clarity and confidence.