CSPM Definition
CSPM, or Cloud Security Posture Management, is a tool or set of practices designed to manage and improve the security stance of cloud environments.
CSPM FAQs
What is CSPM?
CSPM is essential for organizations using cloud services to ensure their environments remain secure, compliant, and protected against potential threats. CSPM tools automatically assess cloud configurations, identify risks, enforce security best practices, and ensure compliance with security policies and standards (like SOC 2, GDPR, or HIPAA).
CSPM works by continuously scanning cloud resources (like virtual machines, databases, storage, etc.) for misconfigurations, policy violations, and vulnerabilities. It can detect issues like open ports, unused resources, excessive permissions, and other potential vulnerabilities, helping prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
How Does CSPM Work?
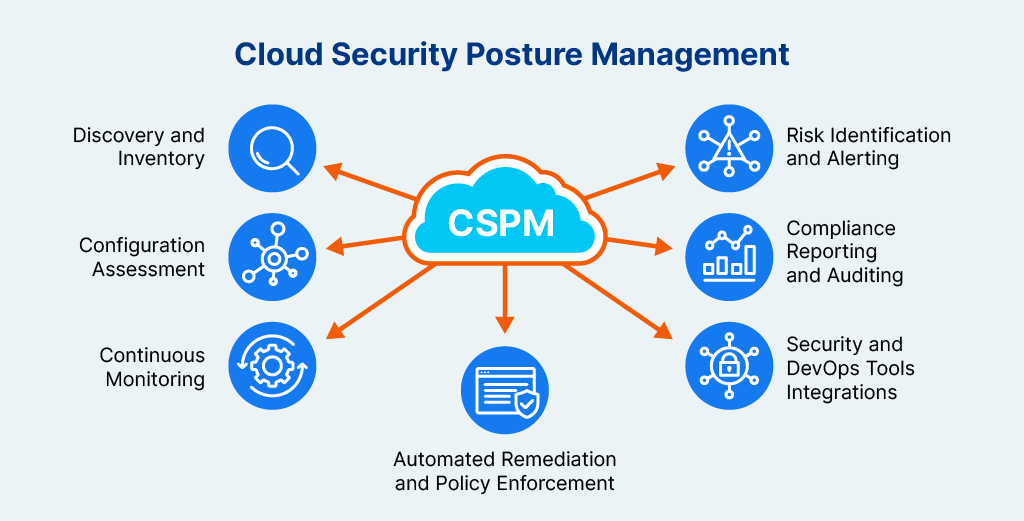
CSPM operates by continuously monitoring and managing the security configurations of cloud environments to prevent misconfigurations, enforce compliance, and detect vulnerabilities. Here’s a breakdown of how CSPM works:
Discovery and Inventory
- CSPM tools first discover and catalog all cloud resources (e.g., virtual machines, databases, storage buckets, network configurations) across multiple cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
- This discovery process provides a centralized view of cloud assets, crucial for visibility in complex, dynamic cloud environments.
Configuration Assessment
- The tool assesses the configurations of resources against security best practices and compliance standards. It examines settings like open ports, firewall rules, encryption status, and access permissions.
- CSPM uses benchmarks from frameworks like the CIS (Center for Internet Security) and applies relevant compliance standards such as SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR to identify policy violations.
Continuous Monitoring
- CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud environments in real-time or near-real-time, tracking any changes in configurations or security posture.
- This continuous scanning helps detect new or updated resources and prevents risky configurations, like exposing databases to the public internet or allowing over-permissive IAM roles.
Risk Identification and Alerting
- CSPM analyzes cloud configurations to identify risks and vulnerabilities. Common risks include excessive permissions, insecure network settings, unencrypted data, and exposed services.
- It prioritizes risks based on severity and potential impact, triggering alerts when a misconfiguration, policy violation, or vulnerability is detected.
Automated Remediation and Policy Enforcement
- Many CSPM tools offer automated or guided remediation to correct security issues, such as automatically removing overly permissive access rights or closing open ports.
- They also support policy enforcement by allowing organizations to set specific policies that prevent non-compliant configurations from being deployed.
Compliance Reporting and Auditing
- CSPM tools provide compliance reports and audit logs to help organizations meet regulatory requirements and internal policies.
- Reports include details on compliance status, policy violations, and remediation actions taken, making it easier to demonstrate adherence to standards during audits.
Integrations with Security and DevOps Tools
- CSPM integrates with other security tools (e.g., SIEM, IAM) and DevOps pipelines to enhance security across the organization.
- For example, integrating with CI/CD tools enables DevOps teams to enforce security policies during deployment, reducing misconfigurations from the start.
Benefits of CSPM
Improved Security. By proactively identifying misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, CSPM strengthens cloud security.
Enhanced Compliance. CSPM helps organizations meet industry and regulatory compliance standards with continuous monitoring and reporting.
Operational Efficiency. Automating remediation and policy enforcement saves time and reduces the burden on security teams.
Risk Reduction. Prioritizing and addressing high-risk configurations reduces the likelihood of data breaches and other security incidents.
CNAPP vs CSPM
Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) and CSPM are both security frameworks for cloud environments, but they focus on different aspects of cloud security and offer unique functionalities. The key differences are:
- Scope: CSPM is narrower, focusing on cloud configuration and compliance, while CNAPP covers the full application lifecycle security, from code to runtime.
- Functionality: CNAPP includes CSPM functions but adds workload protection, vulnerability scanning, CI/CD integration, and application-layer security.
- Use Cases: CSPM is suited for ensuring security posture and compliance in cloud setups. CNAPP is best for end-to-end security in environments with cloud-native applications, including containers, microservices, and serverless architectures.
CNAPP offers a more holistic security approach for cloud-native applications, while CSPM is valuable for maintaining a secure configuration and compliance posture in the cloud. Many organizations use both, with CSPM as a subset of CNAPP.
SSPM vs CSPM
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) and CSPM are two different approaches within cloud security, but each focuses on distinct environments and risks:
- Focus: SSPM targets SaaS applications, while CSPM is focused on cloud infrastructure.
- Environment: SSPM works within third-party SaaS applications (e.g., Microsoft 365, Salesforce), whereas CSPM is concerned with securing resources on IaaS/PaaS platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure).
- Functionality: While both manage security configurations, SSPM is more specialized for SaaS settings, permissions, and user activities, while CSPM targets infrastructure configurations, network settings, and cloud-native resources.
SSPM is specifically designed to secure SaaS applications, while CSPM is geared toward securing cloud infrastructure. Many organizations use both SSPM and CSPM to cover the full scope of their cloud and SaaS environments.
How Does AppOmni Differ From Traditional CSPM?
AppOmni’s focus on SSPM fills a vital role for organizations that use SaaS applications extensively. Our SaaS security platform specializes in providing visibility, security, and compliance for SaaS applications, which is a critical subset of CSPM geared specifically toward managing security in SaaS platforms.
AppOmni is an SSPM solution rather than a full CSPM but offers critical posture management capabilities tailored for SaaS environments, complementing CSPM tools used for cloud infrastructure.