Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) refers to a cybersecurity approach focused on identifying, detecting, and mitigating threats targeting identity and access management (IAM) systems. ITDR specifically aims to address the growing risks associated with compromised identities, which are often a critical attack vector in data breaches and other security incidents.
ITDR FAQs
What is Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR)?
ITDR is a cybersecurity solution designed to detect, analyze, and respond to threats targeting user identities and access management systems. It focuses on preventing identity-based attacks such as credential theft, unauthorized access, and privilege escalation by continuously monitoring and securing user accounts.
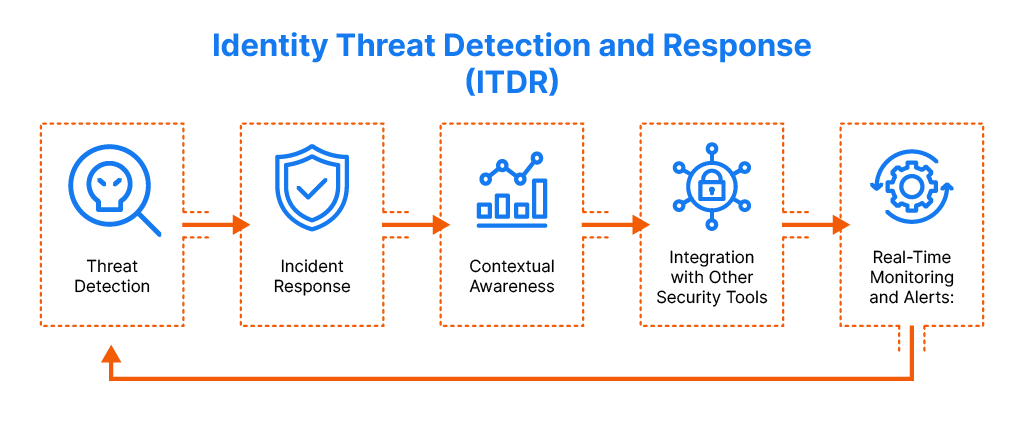
Key Components of ITDR
Threat Detection: ITDR continuously monitors for suspicious behavior or anomalies related to user identities, such as unusual login patterns, privilege escalation, or access to sensitive resources.
Incident Response: Once a threat is detected, ITDR systems initiate response mechanisms to contain and mitigate the impact, such as locking accounts, requiring re-authentication, or alerting security teams.
Contextual Awareness: ITDR tools leverage contextual data like location, device, time of access, and behavior to identify potential threats more effectively, reducing false positives and improving accuracy.
Integration with Other Security Tools: ITDR often integrates with broader security platforms, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Privileged Access Management (PAM), and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), to provide a comprehensive security posture.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: ITDR solutions offer real-time alerts and actionable intelligence to security teams, enabling quicker response to identity-based threats.
Why ITDR is Important
- Rise of Identity-Based Attacks: Cybercriminals increasingly target user credentials and identities to gain unauthorized access to systems. ITDR helps safeguard these critical entry points.
- Zero Trust Architectures: ITDR supports zero-trust security models, which assume that no user or device, inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default.
- Cloud and Remote Work Security: As more organizations move to cloud environments and embrace remote work, ITDR ensures that identities are continuously protected across different environments.
Why You Should Implement ITDR
Implementing ITDR is essential for organizations to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats that target identities. Here are several key reasons to implement ITDR:
Protection Against Identity-Based Attacks
- Identity Compromise: Attackers often target user credentials to gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. ITDR helps detect and mitigate these identity-based threats before they lead to serious breaches.
- Phishing and Credential Theft: With phishing and credential theft on the rise, ITDR can detect anomalies in user behavior that might indicate a compromised account, such as unusual login locations or actions.
Zero Trust Architecture
- Assuming No Trust: In a zero-trust security model, every access request is verified, and no user or device is trusted by default. ITDR complements this approach by continuously monitoring identities and ensuring that even trusted accounts are scrutinized for suspicious activity.
- Least Privilege Enforcement: ITDR helps enforce least-privilege access by detecting and responding to improper privilege escalations, preventing attackers from gaining high-level access to critical resources.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Response
- Early Detection: ITDR provides real-time monitoring of identity systems, enabling the early detection of potential threats, allowing security teams to respond before significant damage occurs.
- Automated Response: ITDR solutions often include automated response mechanisms, such as account lockdown or re-authentication requests, reducing the time between threat detection and mitigation.
Improved Incident Response
- Contextual Awareness: ITDR systems analyze contextual factors (e.g., user behavior, device information, location) to provide better insights into potential threats. This enables faster, more informed responses to incidents.
- Reducing False Positives: By focusing on identity-specific threats and understanding behavioral patterns, ITDR reduces false positives, allowing security teams to prioritize real risks.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
- Meeting Compliance Standards: Many regulatory frameworks (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) require organizations to secure user identities and access control systems. ITDR helps meet these requirements by providing robust identity monitoring and security measures.
- Audit and Reporting: ITDR solutions often include logging and reporting features that can help with compliance audits, providing clear records of identity-related security activities.
Securing Cloud and Hybrid Environments
- Cloud Identity Protection: As organizations migrate to the cloud, managing and securing identities across multiple platforms becomes more complex. ITDR ensures that identities in cloud environments are constantly monitored and protected.
- Remote Workforce: With an increase in remote work, identity-based threats have multiplied. ITDR helps safeguard user identities, even when employees are accessing systems from diverse locations and devices.
Reducing Insider Threats
- Monitoring Privileged Accounts: ITDR solutions track the activity of privileged users, who are often prime targets for insider threats. Any suspicious behavior by these accounts can trigger immediate investigation or automated responses.
- Behavioral Analytics: ITDR uses machine learning and behavioral analytics to identify deviations in typical user actions, which can signal potential insider threats or compromised accounts.
Enhanced Security Posture
- Integrated Security Strategy: ITDR can work alongside other security tools, such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), to provide a comprehensive defense system.
- Proactive Risk Management: Implementing ITDR shifts the organization from a reactive to a proactive security stance, identifying potential risks before they escalate.
ITDR vs EDR
ITDR and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) are both cybersecurity technologies designed to detect and respond to threats, but they focus on different areas of the security landscape:
Focus and Scope
ITDR
- Focuses on identity and access management (IAM), ensuring that user accounts, identities, and privileges are secure.
- Monitors for suspicious or malicious activities related to user credentials, authentication processes, and privileged access.
- Protects against identity-based threats, such as credential theft, phishing, insider threats, and unauthorized access.
EDR
- Focuses on endpoint devices, including laptops, desktops, mobile devices, and servers.
- Monitors and analyzes activity on these devices to detect signs of compromise, such as malware, ransomware, and other malicious activities targeting endpoints.
- Protects against endpoint-based threats, such as malware, fileless attacks, and exploits targeting vulnerabilities on devices.
Primary Threat Vectors
ITDR
- Addresses threats related to user identities and the misuse of credentials.
- Protects against identity theft, privilege escalation, and lateral movement that often result from compromised credentials.
EDR
- Focuses on device-level threats like malware infections, file tampering, and suspicious processes.
- Identifies attacks such as unauthorized software execution, malicious payloads, and exploits targeting endpoint vulnerabilities.
Key Capabilities
ITDR
- Real-time monitoring of login patterns, access requests, and credential usage.
- Uses behavioral analytics to detect anomalies in user behavior.
- Responds to identity-based threats through actions like account lockdowns, re-authentication, or privilege restriction.
EDR
- Monitors endpoints for suspicious activities, like unusual file changes, running processes, or unexpected network connections.
- Includes capabilities for incident response, such as quarantining infected devices, terminating malicious processes, or isolating endpoints from the network.
Attack Mitigation
ITDR
- Focuses on stopping attacks that leverage compromised credentials, insider threats, or identity abuse.
- Prevents attackers from gaining access to systems or escalating privileges by detecting suspicious authentication attempts or unauthorized access.
EDR
- Focuses on blocking and responding to malware, exploits, and other device-based compromises.
- Mitigates attacks by isolating affected endpoints, removing malware, and preventing further lateral movement within the network.
Integration
ITDR
- Often integrates with IAM systems like Active Directory, Single Sign-On (SSO), or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Works closely with Privileged Access Management (PAM) to monitor privileged accounts.
EDR
- Integrates with broader endpoint management tools and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to provide comprehensive endpoint security insights.
- Can work alongside ITDR by securing the devices that users authenticate from.
Threat Examples
ITDR
- A compromised employee account used to access sensitive data after-hours.
- Privilege escalation of a regular user account to admin-level access without proper authorization.
EDR
- A malware infection on an employee’s laptop that is spreading across the network.
- A ransomware attack that encrypts files on an organization’s servers.
Complementary Roles
- ITDR and EDR are complementary in a modern cybersecurity strategy.
- ITDR ensures that identity and access processes are secure, safeguarding against misuse or compromise of credentials.
- EDR ensures that endpoint devices are protected from malware, exploits, and other attacks.
Together, they provide holistic security, covering both identity and device-level vulnerabilities.
How Does AppOmni Approach ITDR?
AppOmni can now take threat detection for SaaS to another level with enhanced SaaS-Aware Identity Threat Detection and Response (SITDR). AppOmni’s SaaS-awareness enhances ITDR capabilities by prioritizing identity in SaaS security. With comprehensive lifecycle visibility into identities within the SaaS environment, including SaaS events, logs, and user behavior, we identify SaaS-specific threats arising from misconfigured permissions, unusual user activities, compromised credentials, and other vulnerabilities.
Read more about AppOmni’s ITDR Solutions.