SaaS misconfigurations are one of the most common causes of data exposure incidents in modern organizations. As businesses rely on cloud-based apps more than ever, even a single overlooked setting in a SaaS application can put sensitive data at risk. Understanding what SaaS misconfigurations are, why they happen, and (most importantly) how to prevent them is essential.
What is a SaaS misconfiguration?
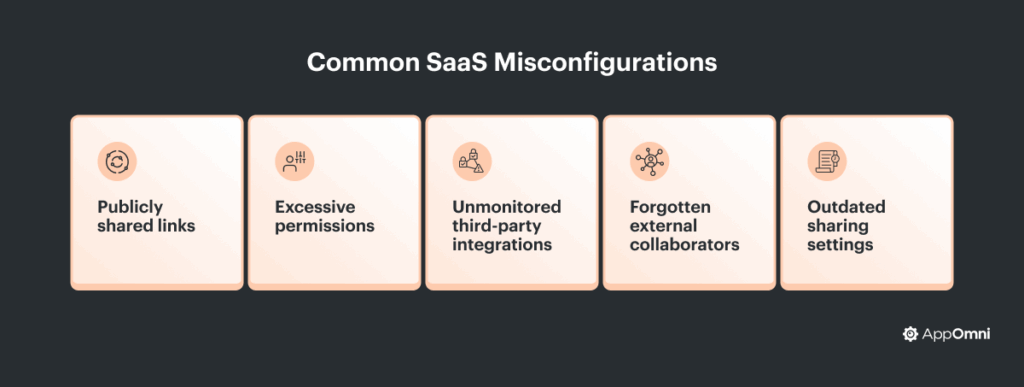
A SaaS misconfiguration is a mistake, oversight, or unintended setting in a SaaS application that puts sensitive data or business processes at risk. These aren’t software bugs. Instead, they’re human or process errors that often go unnoticed without the right visibility and controls. Misconfigurations can be things like leaving the wrong document shared with “anyone with the link,” giving a third-party integration too much access, or failing to update security settings as your organization changes.
Some common examples include:
- Granting broad or admin-level access to users who don’t need it.
- Using default or permissive sharing settings that allow data to be seen externally.
- Leaving old third-party apps or integrations connected after they’re no longer needed.
- Failing to review and update access or sharing as teams and roles evolve.
Misconfigurations don’t exploit weaknesses in the SaaS provider’s code or anything super sophisticated. Essentially, they just happen because something was missed or misunderstood in setup or ongoing management. This simplicity is exactly what makes them so tricky and dangerous.
There are a few common misconceptions worth clearing up:
- “My SaaS vendor handles security for me.” In reality, SaaS providers secure the platform itself, but organizations are responsible for how their data is accessed, shared, and secured within it.
- “Misconfigurations are a one-time risk.” In reality, SaaS environments are always changing, and new misconfigurations can appear at any time.
- “Only admins can create risks.” Any user who can share data or connect new integrations has the potential to expose sensitive information.
Why are SaaS misconfigurations so common?
SaaS has become the operating system of modern business, powering collaboration, workflows, and sensitive data across every function. That central role also makes misconfigurations uniquely impactful if not continuously managed. Most organizations have dozens of SaaS tools in use, each with unique permissions, sharing, and integration settings. Keeping up with it all is a challenge.
There are a few key reasons why misconfigurations are so persistent, according to data from AppOmni’s 2025 State of SaaS Security Report:
- Decentralized ownership: Only 16% of organizations pin SaaS security squarely on the security team. In contrast, 43% delegate it to the business owner of each app, and 41% split it between business and security. Fragmented ownership leaves room for policy drift and conflicting priorities.
- Shadow IT: Even with “sanctioned-apps-only” policies, 22% of organizations admit enforcement is lax. The top driver of unsanctioned adoption is “approval takes too long” (29%), followed by employee unawareness (19%). In short, users still install what they need, when they need it.
- Constant change overwhelms point-in-time reviews: A majority of organizations (52%) still rely on periodic audits, and only 43% have continuous or near-real-time oversight. That gap shows up in incidents: 41% of breaches trace back to permission drift and 29% to misconfigurations (issues that often slip in between audits).
- Misplaced trust fuels a security mirage: 91% of teams say they’re confident in their SaaS posture, yet 75% suffered a SaaS-related incident in the past year. Over half (53%) base that confidence primarily on trust in the SaaS vendor, and 89% of breached organizations believed they already had “appropriate visibility.” Without shared accountability and true visibility, organizations operate under a false sense of security that leaves them vulnerable.
What happens with a misconfiguration? What can go wrong?
When a SaaS misconfiguration slips through the cracks, the consequences can be immediate, far-reaching, and costly. Unlike a traditional software vulnerability that might require a sophisticated exploit, a misconfiguration can expose sensitive data with nothing more than a careless setting or an overlooked permission.
The primary consequences of misconfigurations are:
- Data exposure: It can take many forms, from confidential documents being accessible to anyone with a link, to sensitive records shared with external users, to critical business data exposed to the public internet. Even minor oversights—like granting excessive API or integration permissions—can open the door to data scraping, unauthorized exports, or privilege escalation.
- Operational disruption: When a misconfiguration is discovered (often by accident, or during an incident), IT and security teams are forced to drop everything and scramble to contain the exposure. Investigating what was exposed, to whom, and for how long can be time-consuming and stressful (especially if regulators or customers are involved).
The cost of a SaaS data breach (even from something as small as a misconfiguration)
When SaaS misconfigurations go undetected, organizations can face immediate and costly consequences. According to IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a cloud-related data breach reached $4.75 million, with SaaS misconfigurations among the most common root causes. These costs include not only technical investigations and remediation, but also legal fees, regulatory fines, lost productivity, and long-term reputational damage.
In these cases, organizations can face:
- Data exposure: Confidential documents and records can be exposed to unauthorized users or the public.
- Regulatory penalties: Non-compliance with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA can result in significant fines.
- Business disruption: Teams often have to pause key projects to contain and investigate incidents.
- Reputational damage: Loss of customer trust is common after publicized breaches.
- Litigation: Legal actions from customers, partners, or regulators may follow.
Even for organizations with strong security teams, misconfigurations often happen quietly and go undetected for weeks or months. In the 2025 State of SaaS Security Report, 41% of breaches were traced back to permission drift and 29% to misconfigurations—issues that commonly arise between periodic reviews.
The true cost of a SaaS misconfiguration isn’t just in the headline fines or cleanup. It’s in the trust lost with customers, the business disruption, and the ongoing risk of repeated incidents unless preventive controls are put in place.
Examples of misconfigurations
Even the most careful organizations can fall victim to SaaS misconfigurations because they often happen with no real signs until sensitive data is already exposed. These incidents aren’t caused by sophisticated attackers exploiting obscure bugs, but by simple, everyday settings that slip through the cracks. Below are some real-world examples, showing just how easily a single misstep can put business-critical data at risk.
- Sensitive dashboards left accessible to anyone with the link: Organizations can inadvertently expose internal dashboards containing customer data and support tickets, simply by allowing “public link” access without adequate restrictions. Anyone who guessed or obtained the link could view confidential information, bypassing authentication.
- Over-permissioned third-party apps: Organizations often integrate productivity or workflow tools that request broad access, such as reading all emails or files in user accounts. An example of a misconfiguration incident here would be a third-party integration being granted full access to a company’s calendars and contacts, leading to data being visible to the integration provider’s external support team.
- Unrestricted sharing settings in cloud document platforms: Sensitive spreadsheets, strategy documents, and HR records could be shared with “anyone with the link,” including outside contractors and even indexed by search engines.
- Overly broad API permissions: APIs used for automation or reporting could be configured with admin-level access, meaning that if an API token were leaked or compromised, attackers could extract massive volumes of data or make unauthorized changes.
- Forgotten external collaborators: Over time, contractors or partners who no longer work with your company might still retain access to critical project folders or ticketing systems. This poses an ongoing risk if their credentials were compromised.
These types of exposures don’t require sophisticated hacking. They’re simply the result of common, easily-missed misconfigurations, and they highlight how a single unchecked setting can lead to massive data exposure.
How to reduce your risk for SaaS misconfigurations
Preventing SaaS misconfigurations isn’t just about reacting when things go wrong; it’s about building continuous, proactive processes into your daily operations. Here’s how to make prevention part of your organization’s SaaS security DNA:
1. Know what’s in use (and who’s using it).
Start with a clear inventory of every SaaS app in your environment, including those quietly adopted by business units or individual employees (shadow IT). Automated discovery tools can help surface both sanctioned and unsanctioned applications, as well as connected third-party integrations that might otherwise be missed.
2. Continuously monitor configurations, not just once a year.
Relying on annual or periodic audits leaves huge gaps where risky changes can go unnoticed. Instead, implement continuous or near-real-time monitoring to alert you to new misconfigurations as soon as they appear. This is crucial, since more than half of organizations still depend on point-in-time reviews, even though the SaaS environment is always evolving.
3. Enforce least privilege and strong access governance.
Every user and integration should only have the access they truly need—nothing more. Make it a habit to regularly review and adjust permissions, removing access as roles change or projects end. Be especially careful with admin privileges and integrations that have broad scopes.
4. Standardize secure baselines and onboarding.
Don’t leave new SaaS apps at default settings. Establish and enforce security baselines and templates for each platform, and make security reviews part of the onboarding process. Likewise, offboard users and integrations promptly, revoking access when employees leave or apps are retired.
5. Automate wherever possible.
Manual reviews simply can’t keep up with the scale and speed of SaaS. Automated solutions like AppOmni can continuously scan for risky changes, flag permission drift, alert you to dangerous sharing links, and even help remediate misconfigurations before they lead to exposure.
6. Educate and empower users.
Technical controls are vital, but so is awareness. Provide clear guidance and training so business users and admins understand the risks of improper sharing, over-permissioned integrations, and “set it and forget it” attitudes. When possible, use technical guardrails (such as DLP policies or enforced sharing restrictions) to prevent common mistakes.
7. Build prevention into business-as-usual.
Misconfigurations aren’t a one-time risk. Make prevention a routine part of change management, access reviews, and employee onboarding/offboarding. Regular check-ins and automated reporting can help you spot trouble early and keep teams accountable.
Conclusion
SaaS misconfigurations are now the leading cause of SaaS data exposure events. The good news? They’re entirely preventable. With ongoing visibility, strong access controls, and automated monitoring, you can transform SaaS from a source of hidden risk into a true engine for secure collaboration.
Prevention works best when it’s continuous, automated, and shared across teams—not just a once-a-year project for IT. By combining proactive visibility, ongoing monitoring, least-privilege access, and user education, organizations can dramatically reduce their risk of SaaS misconfigurations and data exposures
Looking for a practical guide to securing your SaaS environment? Take control of your SaaS security now. Learn how to build a solid business case, select the best SSPM vendor, and implement effective protection for your SaaS apps—all before a misconfiguration forces your hand.
SaaS Security Made Simple: Build Your Case, Choose Your Vendor, and Protect Your Data

Take control of your SaaS security now. Learn how to build a solid business case, select the best SSPM vendor, and implement effective protection for your SaaS apps—all before a breach forces your hand.
Read more: SaaS Security Made Simple: Build Your Case, Choose Your Vendor, and Protect Your Data