Privileged Access Management Definition
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a cybersecurity strategy that controls, monitors, and secures access to an organization’s most critical systems and sensitive data. PAM solutions protect privileged accounts (those with elevated permissions beyond standard users) from misuse by managing and enforcing administrative entitlements, including the addition and removal of elevated access, alongside strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and automated credential management.
Privileged Access Management FAQs
What is Privileged Access Management?
Privileged Access Management represents a comprehensive cybersecurity approach that combines people, processes, and technology to safeguard an organization’s most sensitive assets. By enforcing the principle of least privilege and preventing unauthorized access to high-value assets, PAM helps organizations reduce their attack surface and defend against both external threats and insider risks. Enterprise privileged access management addresses the reality that privileged accounts vastly outnumber standard users in modern IT environments, often by a factor of three or four. These accounts exist across on-premises infrastructure, cloud platforms, SaaS applications, and hybrid environments, creating an expansive surface that attackers actively target to reach critical systems and data.
Privileged access management tools provide the capabilities organizations need to discover high-authority accounts, vault credentials securely, enforce just-in-time access policies, and maintain detailed audit logs of all privileged activities. These solutions automate password rotation, eliminate hardcoded credentials in applications, and provide session monitoring to detect suspicious behavior in real time. Privileged access management security extends protection beyond traditional IT administrator accounts to cover service accounts, SSH keys, API keys used by DevOps teams, and emergency “break glass” accounts. Nearly all advanced cyberattacks exploit privileged credentials to move laterally through networks, making PAM essential for defending against both external threat actors and malicious insiders who abuse their elevated permissions.
How Does Privileged Access Management Work?
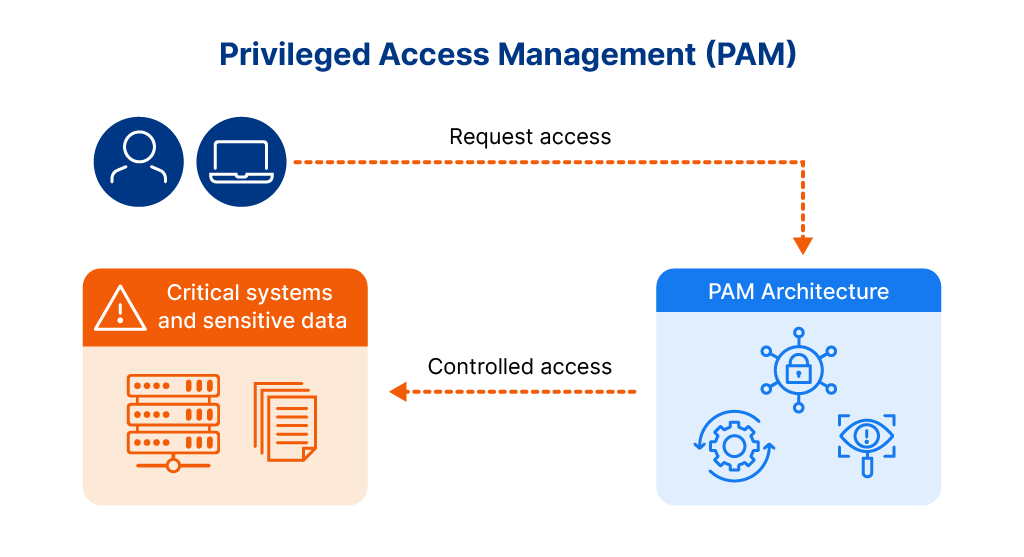
A privileged access manager operates through multiple integrated components that work together to create a secure framework for controlling elevated permissions. At its core, privileged access management architecture typically includes a centralized credential vault that stores and encrypts all privileged passwords, keys, and secrets. This vault becomes the single source of truth for credential management, automatically rotating passwords after each use and eliminating the risk of static credentials being compromised. The architecture also incorporates session management capabilities that record and monitor all privileged user activities, creating detailed audit trails that security teams can review to identify anomalous behavior or policy violations.
Privileged access management products implement several key functions to protect critical resources. They begin by discovering all privileged accounts across the IT environment, including hidden or orphaned accounts that IT teams may not know exist. Once discovered, these accounts are onboarded into the vault where access policies can be enforced. Users requesting privileged access must authenticate through multi-factor authentication (MFA) and receive temporary, just-in-time credentials rather than permanent elevated permissions. The system evaluates each access request based on contextual factors like user identity, device health, location, and the specific resource being accessed before granting approval.
Privileged access management requirements vary by organization but generally include the ability to enforce least-privilege principles, provide comprehensive visibility into privileged activities, support automated workflows for credential lifecycle management, and generate compliance reports for regulatory audits.
Privileged access management implementation typically follows a phased approach: organizations start by securing their most critical assets – such as domain controllers and production databases – before expanding coverage to additional systems. This allows security teams to demonstrate rapid risk reduction while building expertise with the platform. Successful implementations integrate PAM solutions with existing identity providers, SIEM systems, and ticketing platforms to create a cohesive security ecosystem that scales across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments.
Why Is Privileged Access Management Important?
Privileged accounts represent the most attractive targets for cybercriminals because they provide direct pathways to an organization’s most valuable assets. Without a robust privileged access management strategy, organizations face devastating consequences from both external attackers and malicious insiders. Nearly every major data breach in recent years has involved the exploitation of privileged credentials. Attackers who steal or compromise privileged accounts can operate undetected as legitimate administrators, moving laterally across networks, accessing sensitive databases, exfiltrating confidential data, and deploying ransomware that can cripple entire operations.
The risks extend beyond external threats. Insider threats pose an equally serious danger when privileged access goes unmanaged. Disgruntled employees with excessive permissions can delete critical data, steal intellectual property, or sabotage systems before departing the organization. Even well-intentioned insiders create risk through accidental misconfigurations or by falling victim to social engineering attacks that trick them into revealing their privileged credentials.
Without PAM controls, organizations also struggle to meet compliance requirements and face significant financial penalties. Regulations like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR mandate strict controls over who can access sensitive data and require detailed audit trails of privileged activities. Organizations lacking these controls cannot demonstrate compliance during audits, leading to fines, legal liability, and reputational damage. A comprehensive privileged access management strategy transforms privileged accounts from the organization’s greatest vulnerability into a defensible security layer that protects the business from catastrophic losses.
Benefits of Privileged Access Management
Organizations that implement comprehensive PAM programs experience significant security improvements and operational advantages that extend across their entire IT infrastructure. Leading companies that provide privileged access management solutions have developed solutions that deliver measurable value by addressing the full lifecycle of privileged credentials and sessions. These benefits accumulate over time as PAM programs mature, creating a foundation for secure digital transformation initiatives.
Key Benefits for Enterprises and SaaS Providers:
- Reduced cyber risk and smaller attack surface – Eliminating unnecessary privileged access and enforcing least-privilege principles dramatically limits the pathways attackers can exploit to compromise critical systems.
- Prevention of credential theft and lateral movement – Automated credential rotation and session isolation stop attackers from using stolen credentials to move between systems and escalate privileges.
- Enhanced visibility and threat detection – Continuous monitoring of privileged sessions combined with behavioral analytics enables security teams to identify suspicious activities and respond to incidents before they cause damage.
- Simplified regulatory compliance – Comprehensive audit trails and automated access controls help organizations meet requirements for SOX, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and other frameworks while reducing the time and resources needed for compliance reporting.
- Lower operational costs and complexity – Automating password management, access provisioning, and session recording eliminates manual processes that consume IT resources and introduce human error.
- Protection against insider threats – Granular access controls and session monitoring detect both malicious insiders abusing their privileges and accidental misconfigurations by well-meaning administrators.
- Secure cloud and hybrid environments – PAM extends consistent security policies across on-premises infrastructure, public cloud platforms, and SaaS applications, ensuring privileged access remains protected regardless of where resources reside.
- Faster incident response and forensics – Detailed session recordings and activity logs provide security teams with the evidence needed to investigate breaches quickly and understand exactly what occurred during security incidents.
Risks of Not Using Privileged Access Management
Organizations that fail to implement proper privileged access controls expose themselves to severe security vulnerabilities that threat actors actively exploit. Privileged access management risks compound over time as IT environments grow more complex and interconnected, creating blind spots where unmonitored privileged accounts can become entry points for devastating attacks. Without PAM, companies lack visibility into who has elevated permissions, what those privileged users are doing, and whether credentials have been compromised or misused.
The most immediate danger comes from unmanaged credentials that remain static and easily exploitable. Attackers who gain access to just one privileged account can leverage those credentials to move laterally across the network, escalating their privileges until they reach domain controllers or critical databases. Default administrator accounts on workstations and servers provide convenient footholds that allow attackers to hop from system to system, stealing additional credentials along the way. Hardcoded passwords embedded in applications and scripts represent another critical vulnerability – once discovered, these credentials give attackers persistent access that remains undetected for months or years.
Organizations without PAM also struggle to contain insider threats, whether malicious or accidental. IT administrators with permanent, unrestricted access to production systems can cause catastrophic damage through deliberate sabotage or simple mistakes. Former employees whose privileged accounts weren’t properly deprovisioned can retain access to sensitive systems long after leaving the company. Service accounts with excessive permissions create additional risk because they often lack the oversight applied to human accounts, making them prime targets for attackers who understand they’re rarely monitored. These privileged access management risks ultimately threaten business continuity, customer trust, and the organization’s long-term viability.
Privileged Access Management Solutions
Privileged access management software has evolved to address the complex security challenges facing modern enterprises, with solutions available as both cloud-based SaaS offerings and on-premises deployments. A comprehensive privileged access management framework typically encompasses several core components working together: privileged session management that controls and records high-risk user activities, credential vaults that secure passwords with automated rotation workflows, and privileged threat analytics that analyze behavior to identify anomalies indicating compromised accounts or insider threats. These platforms provide integrated capabilities to discover, secure, monitor, and manage privileged access across traditional data centers, public cloud platforms, and SaaS applications, creating searchable audit trails that support both compliance requirements and forensic investigations.
Privileged access management services extend beyond technology to include strategic consulting, implementation support, and managed security operations that help organizations build effective PAM programs. Organizations should look for solutions that support their specific environment needs, including capabilities for securing SSH keys on Unix and Linux systems, protecting DevOps secrets in CI/CD pipelines, managing cloud platform credentials, and isolating access to SaaS applications with shared administrative accounts that require multi-factor authentication and continuous monitoring.
Extending PAM to SaaS Security
AppOmni extends privileged access management principles into SaaS environments where traditional PAM solutions cannot reach. The SaaS security platform provides continuous visibility into privileged accounts, administrative roles, and excessive permissions across critical SaaS applications like Salesforce, Microsoft 365, ServiceNow, and Google Workspace. With automated detection of misconfigurations, over-privileged users, and risky third-party integrations, AppOmni enables security teams to enforce least-privilege access at the application level, addressing the gap where most privileged access management strategies end at the network edge. By combining identity-aware monitoring, AI-powered threat detection, and comprehensive SaaS security controls, AppOmni ensures that privileged access remains protected throughout your entire cloud ecosystem, defending the applications and data that power modern business operations.