Microsoft 365 security and Microsoft security monitoring are critical for more than 3.7 million companies worldwide that rely on the platform every day. Microsoft’s expanded audit logs across Exchange Online, SharePoint, and Teams provide deeper visibility into user and application activity. The challenge is knowing which high-risk behaviors to detect and monitor before threats escalate.
Why Expanded Microsoft 365 Logs Matter Now
- Microsoft has expanded audit logs across Exchange Online, SharePoint, and Teams, increasing visibility into critical activity
- Security teams can now monitor email access, search behavior, messaging activity, and file interactions in greater detail
- Expanded logs enable earlier detection of suspicious behavior before incidents escalate
- Broader log coverage supports stronger Microsoft 365 security monitoring without relying solely on reactive alerts
- When paired with the right detections, expanded logs improve threat response and support compliance efforts
The Challenge: Visibility Without Clear Detections
Native Microsoft 365 logs generate large volumes of data across multiple services. Manually reviewing this activity is time-consuming and often impractical for security teams managing multiple priorities.
Attackers take advantage of this complexity by blending into normal user behavior. They may read emails instead of downloading them, search for sensitive terms, or quietly access Teams content without triggering obvious alerts.
To reduce risk, organizations need a focused approach that highlights the most meaningful security signals across Microsoft 365.
10 High-Risk Activities Every Security Team Should Monitor in Microsoft 365
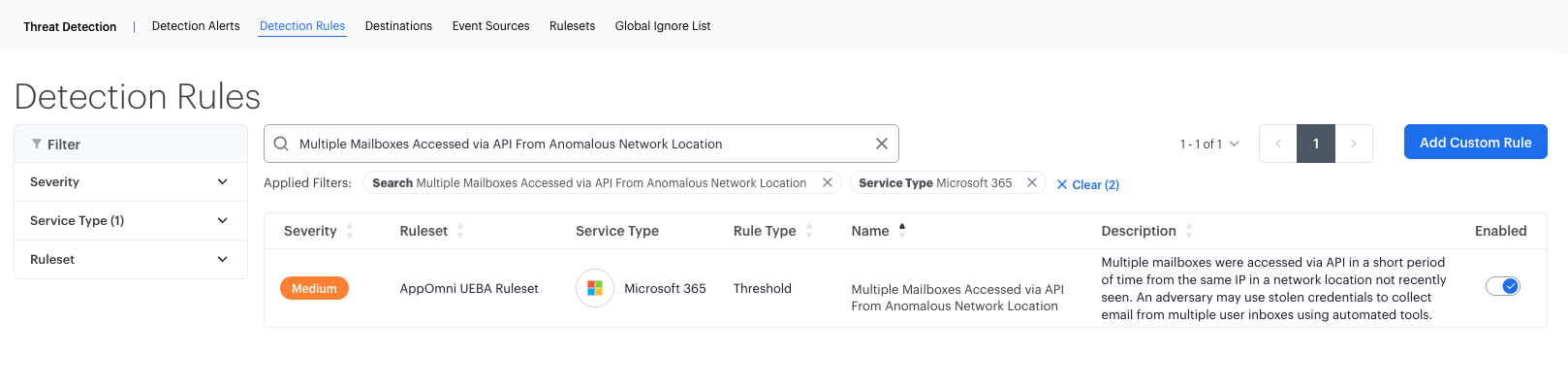
1. Exchange Online: MailItemsAccessed
Attackers who compromise accounts often read emails to gather intelligence, steal sensitive data, or prepare for phishing and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.
Monitor for:
- An AppID accessing multiple mailboxes in a short time frame, which may indicate automated data theft
- Large spikes in mail access activity from a single user, a common sign of account compromise
- Access to sensitive mailboxes from unusual IPs or devices, suggesting external threat actor activity
2. Exchange Online: Send
Attackers often use a compromised email account to send phishing emails, forward sensitive information, or communicate with other compromised users within an organization.
Monitor for:
- Emails sent from known suspicious IP addresses
- Unusual attachment types, such as password-protected ZIP files
- Emails sent from accounts that recently logged in at odd hours or from unexpected locations
3. Exchange Online: SearchQueryInitiatedExchange
Attackers frequently search a compromised mailbox for financial data, credentials, or business-critical information to use for further exploitation.
Monitor for:
- Searches for sensitive terms like “invoice,” “password,” or “wire transfer” by unauthorized users
- Excessive search activity within a short period, which could indicate reconnaissance behavior
- Searches originating from devices or IPs not previously associated with the user
4. SharePoint Online: SearchQueryInitiatedSharePoint
SharePoint and Teams store critical business documents, including financial records, intellectual property, and confidential reports. Attackers search these repositories for valuable information to steal or exploit.
Monitor for:
- Searches for confidential documents performed outside normal working hours
- Queries for sensitive terms by users who are not part of the authorized team or department
- Repeated searches across multiple SharePoint sites by a single user, potentially indicating an insider threat
5. Microsoft Teams: MeetingParticipantDetail
Unauthorized access to virtual meetings can expose sensitive discussions, provide attackers with reconnaissance opportunities, or facilitate social engineering attacks.
Monitor for:
- External or unauthorized users joining meetings related to sensitive topics
- Patterns of participants repeatedly leaving and re-joining meetings, which may suggest eavesdropping attempts
- Meeting participant IPs that match known threat actor infrastructure
6. Microsoft Teams: MessageSent
Attackers often use Teams messages to distribute phishing links, spread malware, or communicate within a compromised organization.
Monitor for:
- High volumes of messages sent to external or guest users
- Messages sent during off-hours or from devices that have not been previously used by the sender
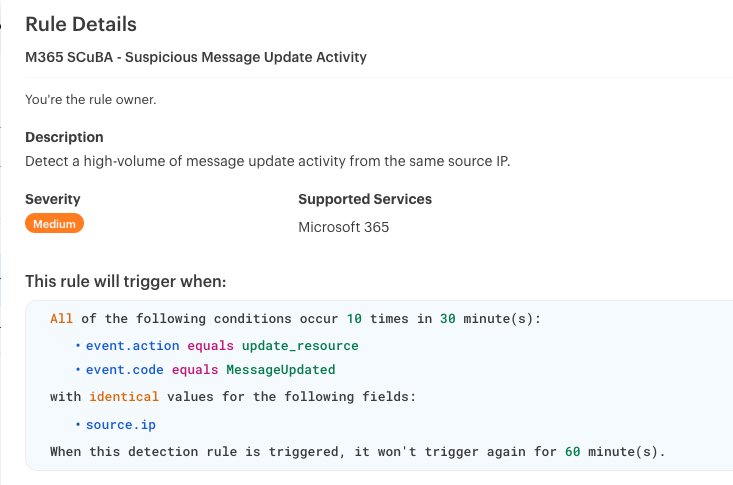
7. Microsoft Teams: MessageUpdated
Edited messages can be a sign of tampering, an attempt to cover up malicious activity, or an effort to mislead other users.
Monitor for:
- Edits made from unrecognized or suspicious IP addresses
- Messages that are repeatedly edited within a short timeframe

8. Microsoft Teams: MessageRead
Attackers who gain unauthorized access to an account may read Teams messages to collect intelligence without actively participating in conversations.
Monitor for:
- Bulk reading of multiple messages in a single chat thread
- Message reads from unauthorized applications or devices
- Messages accessed from IP addresses that do not align with the user’s historical activity
9. Microsoft Teams: ChatRetrieved
The Graph API can be used to silently retrieve chat metadata, giving attackers insight into internal communications, team structures, and high-value targets.
Monitor for:
- Automated retrieval of multiple chat threads by the same AppID
- Chat retrieval requests from unauthorized or unrecognized applications
- Patterns that indicate bulk API activity occurring within a short period
10. Microsoft Teams: MessageHostedContentRead
Attackers may extract files, images, or code snippets from Teams channels to gather sensitive data without triggering standard file download alerts.
Monitor for:
- Access to hosted content by unauthorized external applications
- Repeated retrievals of hosted content from the same chat or channel
- Unusual access patterns related to specific content types, such as proprietary code or financial documents
How AppOmni helps secure Microsoft 365 with Holistic Microsoft Security Monitoring
Manually monitoring Microsoft 365 activity at scale is complex. AppOmni simplifies Microsoft 365 security by turning expanded audit logs into actionable detections.
With AppOmni, security teams can:
- Automate monitoring and alerting for security events across M365 and other SaaS applications, reducing manual work.
- Apply customizable detection rules without needing complex queries or specialized expertise.
- Correlate activity across multiple SaaS platforms to identify meaningful patterns and real threats faster.
- Integrate with SIEM and SOAR solutions to streamline workflows and simplify response efforts.
- Conduct automated compliance checks that make meeting industry standards like NIST, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 easier.
With built-in expertise, clear guidance, and automation, AppOmni makes securing SaaS environments easier and more effective than ever.