CTEM Definition
Continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) is a security management process that exposes an organization’s assets, systems, and networks to ongoing attack simulations to uncover security risks and identify vulnerabilities.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management FAQs
What is an CTEM?
CTEM proactively identifies cyber threats across an organization’s digital ecosystem to allow security teams to analyze and mitigate threats by reducing incidents and their potential impact. The goal is to reduce an organization’s risk exposure and exploitability, and improve security posture.
Continuous threat and exposure management integrates several key components:
Continuous monitoring. CTEM solutions scan organizational infrastructure, applications, and data including network traffic, system logs, and threat intelligence feeds for malicious activity or vulnerabilities.
Threat detection. Anomaly detection, behavioral analysis, and machine learning algorithms help identify potential threats before attackers can cause significant harm.
Vulnerability management. CTEM conducts regular scans, patches known vulnerabilities, and implements best practices to reduce the attack surface and minimize the risk of exploitation.
Configuration management. The CTEM approach configures assets to meet or exceed security standards. This should include a regular review and update of configurations, and enforcement of access controls to prevent unauthorized access and configuration drift.
Response and remediation. CTEM provides an incident triage, forensics analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery framework that minimizes potential impact and prevents future recurrences.
Posture validation. CTEM offers an evaluation of security strategies, controls, and defenses to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and risks.
Security teams use the CTEM approach to:
- Proactively improve threat visibility and situational awareness for prioritized response efforts from security teams with real-time visibility into their security posture
- Enhance incident response capabilities with a structured framework that allows for more timely reactions
- Comply with regulatory requirements such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) with a systematic approach to managing cyber threats
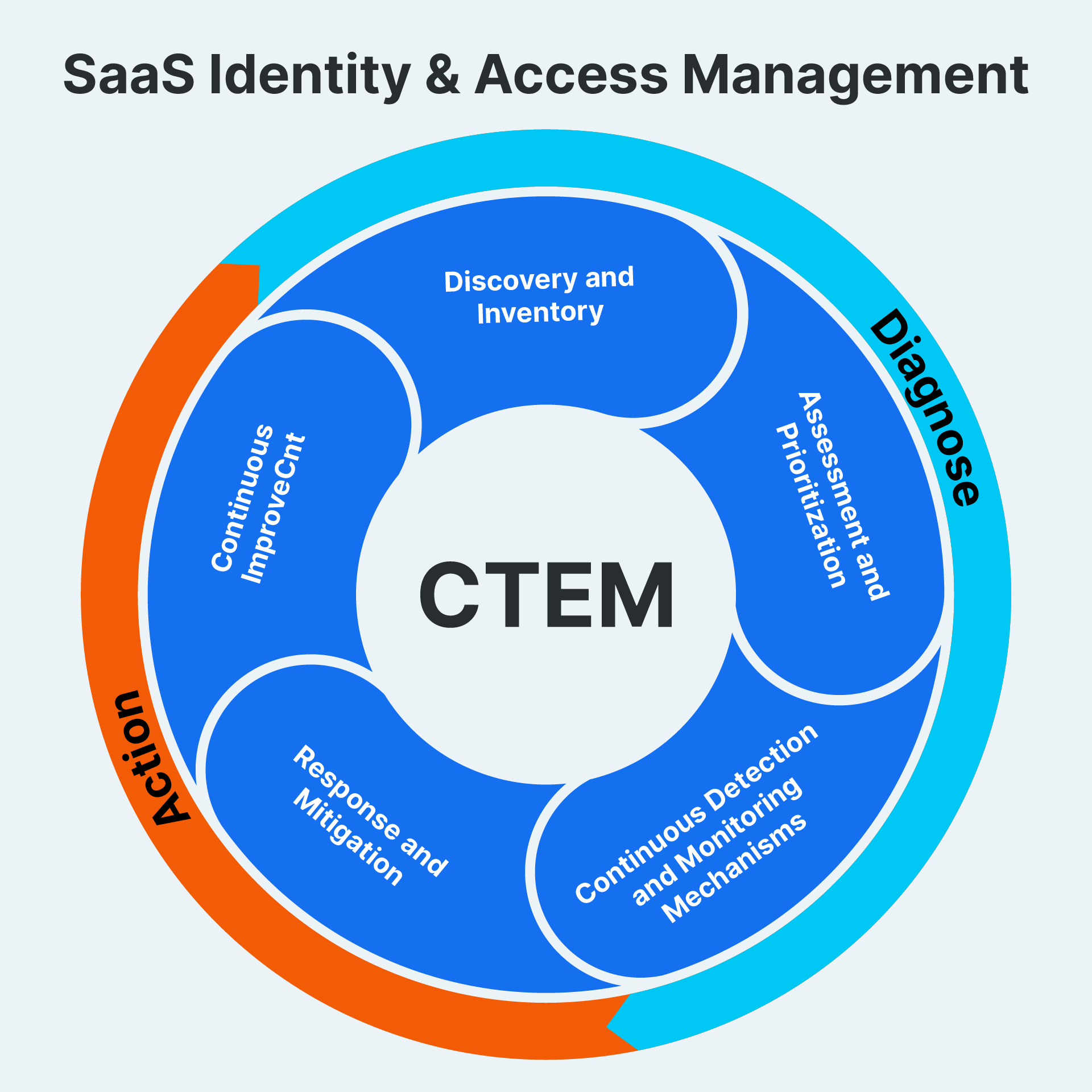
What Are the 5 Stages of CTEM Cybersecurity?
As conceived by Gartner in 2022, the 5 stages of continuous threat and exposure management (CTEM) in cybersecurity typically include:
Discovery and inventory. The first stage of CTEM involves identifying and cataloging hardware, software, applications, data, and any other digital assets.
Assessment and prioritization. Next, the security team looks for exploitable points in organizational assets, prioritizing weaknesses based on potential impact and likelihood of occurrence so they can address the most critical risks first.
Continuous detection and monitoring mechanisms. Intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) platforms identify suspicious activities and anomalies in real-time and are essential to CTEM.
Response and mitigation. CTEM addresses incident response by isolating compromised systems, removing malware, restoring affected data, and implementing security patches or configuration changes to prevent future occurrences.
Continuous improvement. CTEM involves ongoing evaluation and refinement of cybersecurity practices to adapt them to the changing threat environment. This includes analyzing cyber threats and near-misses to identify areas for optimization, and leveraging threat intelligence to outpace emerging attacks.
What Are the Benefits of a CTEM Framework?
Deploying a CTEM model can significantly impact incident response and cybersecurity strategies:
- Proactive CTEM risk management mitigates security risks in real-time, before they are exploited, reducing their potential impact.
- Improved threat detection and response quickly identifies and contains security incidents, minimizing damage and reducing downtime.
- A structured framework offers enhanced incident response capabilities, restoring normal operations more quickly.
- CTEM real-time visibility and situational awareness into emerging threats allow organizations to prioritize response efforts and make informed decisions to improve their overall cybersecurity posture.
- A CTEM framework offers reduced security risk and demonstrates clear compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- CTEM provides continuous feedback and insights into organizational security practices for a culture of continuous improvement that helps organizations adapt their cybersecurity posture over time.
Best Practices for CTEM Security
There are several best practices security teams can follow to effectively implement CTEM and manage cybersecurity risks:
Maintain a comprehensive inventory of digital assets to break up silos, ensure full visibility into the attack surface, and ensure optimal prioritization of tasks.
Conduct vulnerability assessments to identify potential cyber threats and enable prioritization of repairs and patch management based on risk severity.
Deploy robust monitoring solutions to detect signs of malicious activity in the digital environment and allow for real-time responses.
Develop a detailed incident response plan and communicate its details to teams. Conduct regular drills and tabletop exercises to ensure security teams can handle cyber threats.
Provide ongoing employee security training on common cyber threats, phishing scams, and best practices for protecting sensitive information. Empower employees to recognize and report security incidents promptly.
Implement strong access controls and the principle of least privilege to limit the damage radius of attacks. Regularly review and restrict user permissions to limit access based on job responsibilities.
Security by design. Implement secure coding practices, review software and application security, and deploy controls and mitigation to address potential vulnerabilities.
Leverage threat intelligence to proactively defend against emerging cyber threats.
Conduct regular security assessments and audits to identify weaknesses, prioritize remediation efforts, and strengthen the overall security posture.
What is Continuous Threat Exposure Management in the Context of the Cloud?
In the context of the unique threat landscape of cloud and software as a service (SaaS) environments, CTEM presents both new opportunities and challenges for cybersecurity:
Shared responsibility model. The cloud service provider (CSP) typically secures the underlying cloud infrastructure, but it cannot control all data, applications, and configurations within the cloud environment. Most of these are generally the customer’s responsibility, and this introduces risk.
Elasticity and scale. Cloud environments allow organizations to rapidly deploy and scale resources based on demand, but this dynamism makes maintaining visibility and control over cloud infrastructure challenging, and expands opportunities for gaining unauthorized access.
Multi-tenancy. SaaS applications often feature shared infrastructure and resources between multiple customers. This optimizes resources and saves money, but without proper isolation and security controls may also increase the risk of data leakage and cross-tenant attacks.
Complexity of leveraging services across environments. Using hybrid and multiple cloud providers across environments introduces challenges in identity and access management (IAM) and data protection, and increases the likelihood of misconfigurations and security gaps.
Use of the cloud and SaaS solutions increases the organizational attack surface. Attackers may target cloud infrastructure, SaaS applications, data stored online, or connections between users and cloud environments.
Potential threats in cloud and SaaS environments include:
- Data breaches and external cyberattacks
- Compromise of cloud account or other credentials may lead to data theft, service disruption, or lateral movement within the cloud environment
- Misconfigurations in cloud services and SaaS applications
- Insider threats from employees or contractors with access to cloud resources, both malicious and negligent
- Volumetric or application-layer denial of service (DoS) attacks impact availability and performance for cloud services or SaaS applications
- Malware and ransomware infection of cloud resources or SaaS applications may result in data encryption, extortion, or data destruction
How Does a CTEM Approach Compare to Alternative Management Programs?
Here we focus on how the comprehensive and broad capabilities of the CTEM approach compare to more focused management programs such as vulnerability management, red teaming, penetration testing, and external attack surface management (EASM) that also attempt to address cyber threats and are considered to be components of CTEM.
CTEM vs. Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management identifies and prioritizes security weaknesses within systems and applications, while CTEM is focused on broader monitoring and security concerns, including testing configurations and other potential weaknesses.
CTEM vs. Red Teaming
During red teaming exercises, testers simulate cyberattacks to evaluate weaknesses in the security posture as part of a CTEM approach. This offers insight into the resilience of existing CTEM measures against complex cyber threats, and how teams might improve their overall incident response.
CTEM vs. Penetration Testing
During penetration testing, controlled hackers systematically assess security by exploiting system, network, and application vulnerabilities using automated and manual tools. Penetration testing alone offers vital insights, but together with vulnerability management and red teaming it is a critical component of CTEM, providing a comprehensive view into organizational security posture.
CTEM vs. External Attack Surface Management (EASM)
EASM programs are components of CTEM that identify and monitor external-facing assets such as APIs, web applications, and cloud services to reduce the attack surface and mitigate potential security risks. Integrating EASM with other CTEM cybersecurity measures such as continuous monitoring and threat detection more effectively protects the external attack surface and mitigates potential cyber threats.
How Does AppOmni Compare to Various CTEM Vendors?
AppOmni offers SaaS Security Posture Management including threat detection—in-depth visibility into cloud and SaaS activities and event streams to identify threats and potential security exposures that may compromise cloud and SaaS environments before they are exploited. AppOmni continuously monitors SaaS platforms against security policies, allowing organizations to receive alerts automatically if suspicious activity—such as several failed login attempts from different IP addresses in rapid succession—is detected. AppOmni also prioritizes security tasks based on their potential impact on business-critical functions and streamlines the process to meet compliance requirements through automated audits and reporting. Scalable solutions and deeper insight into the SaaS ecosystem help security and IT teams reduce the odds of severe and costly data breaches drastically.
Learn more about the advanced insights AppOmni’s threat detection offers, and why it’s both simpler and much more advanced than CTEM solutions.