Zero Trust Definition
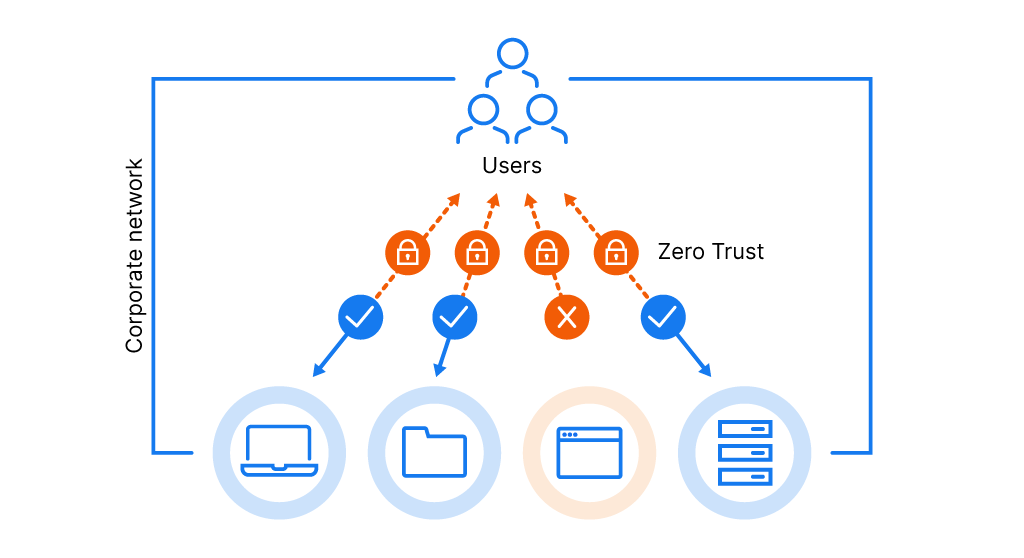
Zero trust security is a cybersecurity framework built on the principle that no user, device, or system should be automatically trusted, regardless of its location inside or outside the network perimeter. Rather than assuming everything within a corporate network is safe, zero trust cybersecurity requires continuous verification of every access request to applications, data, and resources before granting permissions.
This approach eliminates the traditional “castle-and-moat” model where entities behind the firewall were implicitly trusted. Instead, the zero trust model treats every connection as potentially hostile, constantly validating identity and security posture throughout each session to protect against modern security threats.
Zero Trust FAQs
What is Zero Trust?
Zero trust is a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that fundamentally changes how organizations approach access control and data protection. At its core, a zero trust architecture operates on three foundational principles: verify explicitly using all available data points, apply least-privilege access to limit permissions, and assume breach by minimizing potential damage through segmentation and continuous monitoring. Rather than granting broad network access based on a single authentication event, the zero-trust security model requires ongoing verification for every resource request. This means users connect directly to specific applications they need rather than to the entire network, preventing lateral movement if credentials become compromised.
Zero trust access goes beyond traditional perimeter security by evaluating multiple contextual factors, including user identity, device health, location, and behavior patterns – before allowing connections. This dynamic approach adapts in real time as conditions change throughout a session. Zero trust data protection extends these principles to safeguard sensitive information wherever it lives, whether in SaaS applications, cloud environments, or on-premises systems. By implementing continuous authentication and enforcing granular policies, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface while supporting modern work environments that span remote locations, mobile devices, and cloud services.
What Are the Zero Trust Principles?
Zero trust principles provide the foundation for implementing a modern security framework that protects organizations against evolving threats. The three core principles established by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guide how organizations should approach access and security:
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points rather than making assumptions. This means evaluating user identity, device compliance, location, application sensitivity, and data classification before granting access. Every request is treated as if it originates from an untrusted network, requiring validation even for users who were previously authenticated.
- Use Least Privilege Access: Limit user access with Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Access (JIT/JEA) principles, ensuring users only receive the minimum permissions necessary to complete specific tasks. Risk-based adaptive policies continuously adjust access rights based on context, and permissions are revoked immediately when no longer needed. This approach prevents over-privileged accounts from becoming security liabilities.
- Assume Breach: Operate under the assumption that threats already exist within your environment. Minimize blast radius through network segmentation, verify end-to-end encryption for all communications, and use analytics to gain visibility across your infrastructure. This principle drives continuous monitoring to detect threats quickly and limit the damage attackers can cause if they gain initial access.
Beyond these core principles, many security frameworks organize zero trust implementation around five key pillars that address different aspects of an organization’s infrastructure:
- Identities (users and service accounts)
- Devices (endpoints and IoT)
- Networks (segmentation and access control)
- Applications and workloads (cloud and on-premises)
- Data (classification and protection)
By applying zero trust principles across all five pillars, organizations create a comprehensive security posture that adapts to modern hybrid and cloud environments.
What is Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero trust architecture (ZTA) is a comprehensive design and implementation strategy for IT systems that challenges the outdated notion of trusting users and devices simply because they’re connected to a corporate network. Even when users are on a privileged network like a corporate LAN or have been previously verified, a zero trust network architecture maintains that they should not be trusted by default.
Modern corporate networks have become increasingly complex, consisting of interconnected zones, cloud services, remote work environments, mobile devices, and IoT systems. Traditional approaches that rely on VPN connections or assume trust within the corporate perimeter are no longer adequate for these distributed environments. Zero trust architecture addresses this by implementing several key technical approaches:
- Enhanced Identity Governance and Policy-Based Access Controls: Zero trust authentication requires mutual authentication where both user identity and device integrity are verified regardless of location. Access to applications and services is granted based on confidence levels derived from identity verification, device status, and contextual factors like policy compliance and device health.
- Microsegmentation: Zero trust segmentation divides networks into smaller, isolated zones to contain potential breaches and prevent lateral movement. Rather than allowing broad network access, microsegmentation ensures users and systems can only reach the specific resources they’re authorized to use, limiting an attacker’s ability to move through the environment.
- Software-Defined Perimeters and Overlay Networks: Zero-trust network access (ZTNA) creates secure connections between users and applications without placing them on the broader network. This approach uses software-defined perimeters that make applications invisible to unauthorized users while providing seamless, direct access for validated entities.
A complete zero trust architecture implementation typically incorporates elements from all three approaches, establishing strong identity verification, validating device compliance before granting access, and enforcing least-privilege access to explicitly authorized resources. This layered strategy adapts to the realities of modern hybrid and cloud-first infrastructures where traditional network boundaries no longer exist.
What is Zero Trust Segmentation?
Zero trust segmentation is a security technique that divides networks and cloud environments into isolated zones to prevent unauthorized lateral movement and contain potential breaches. Unlike traditional network segmentation that relies on physical boundaries or VLANs, zero trust segmentation applies granular access controls based on identity, application, and workload rather than network location. This approach ensures that even if an attacker gains initial access to one part of the environment, they cannot freely move to other resources.
How Zero Trust Segmentation Works
Zero trust segmentation operates by creating secure boundaries around individual applications, workloads, or data repositories. Each segment has its own access policies that enforce zero trust security principles verifying identity, evaluating context, and applying least-privilege access before allowing any communication between segments. For example, a compromised user account in the marketing department would be restricted to only the applications that account is authorized to access, preventing access to sensitive systems in finance or engineering.
Benefits of Segmentation in a Zero Trust Strategy
Implementing zero trust segmentation significantly reduces the blast radius of security incidents by limiting how far threats can spread. When combined with continuous monitoring and authentication, segmentation helps security teams detect anomalous behavior more quickly since any attempt to access unauthorized segments triggers alerts. This approach is particularly valuable in cloud and hybrid environments where workloads are distributed across multiple platforms and traditional perimeter defenses are ineffective.
How to Implement Zero Trust
Implementing zero trust security requires a strategic, phased approach rather than attempting to overhaul your entire security infrastructure at once. Organizations should begin by identifying their most critical assets and data, understanding who needs access to them, and mapping current access patterns to uncover potential vulnerabilities. This assessment phase helps prioritize which systems and applications should be protected first under a zero trust framework.
The next step involves deploying foundational technologies that enable zero trust principles. This includes implementing strong identity and access management solutions with multi-factor authentication, establishing continuous monitoring and logging capabilities, and deploying tools that can enforce granular access policies. Organizations should focus on connecting users directly to applications rather than placing them on the network, which prevents lateral movement and reduces the attack surface.
How to implement zero trust security successfully also requires cultural change and ongoing refinement. Security teams must work closely with IT and business units to ensure policies balance security with user productivity. Start with a pilot project on non-critical systems to test policies and workflows, then gradually expand coverage across the organization. Continuous evaluation and adjustment of access policies based on real-world usage patterns and emerging threats ensure the zero trust model remains effective as the business and technology landscape evolves.
Zero Trust Security Solutions
Zero trust security solutions encompass a range of technologies designed to enforce continuous verification, least-privilege access, and breach containment across modern IT environments. The best zero trust solutions don’t rely on a single product but rather integrate multiple security capabilities that work together to verify identities, validate devices, secure networks, protect workloads, and safeguard data. Organizations typically need a combination of these tools to build a comprehensive zero trust architecture that addresses their unique security requirements.
Core Zero Trust Solution Categories
Identity and access management (IAM) platforms form the foundation of most zero trust solutions, providing single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, and policy-based access controls. Zero trust network access (ZTNA) solutions replace traditional VPNs by creating secure, direct connections between users and specific applications without exposing the broader network. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools continuously monitor device health and behavior to ensure only compliant, secure devices can access corporate resources. Cloud access security brokers (CASB) and secure web gateways extend zero trust principles to SaaS applications and internet traffic, inspecting data in motion and enforcing policies across cloud services.
Emerging Solutions for Modern Environments
As organizations embrace cloud-native architectures and SaaS applications, zero trust solutions have evolved to address these distributed environments. Cloud workload protection platforms secure communications between microservices and containers, while data security posture management tools discover and classify sensitive information across cloud storage and SaaS platforms. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems and extended detection and response (XDR) platforms aggregate signals from across the zero trust ecosystem to provide the visibility and analytics needed for continuous monitoring and threat detection. The most effective implementations combine these capabilities into an integrated security stack rather than relying on disparate point solutions that create gaps in coverage.
AI for Zero Trust
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing zero trust implementation by enabling organizations to process the massive volumes of contextual data required for continuous verification at scale. AI for zero trust leverages machine learning algorithms to establish behavioral baselines for users, devices, and applications, detecting anomalies that might indicate compromised credentials, insider threats, or policy violations. These systems analyze patterns across access times, locations, resource requests, and device characteristics to calculate risk scores in real time, automatically adjusting access policies as context changes. Beyond detection, AI automates the enforcement of least-privilege principles by recommending appropriate permission levels based on role analysis and peer comparisons, while reducing alert fatigue through intelligent correlation of security events across multiple systems.
Extending Zero Trust to SaaS Security
AppOmni extends zero trust into SaaS applications with Zero Trust Posture Management (ZTPM), addressing the critical security gaps that network-focused solutions miss. The SaaS security platform delivers continuous monitoring of application configurations, user activities, and third-party integrations—going beyond simple device malware checks to provide ongoing security validation of the activities being performed within your SaaS environment. With granular visibility into access decisions at every permission level and AI-powered threat detection, AppOmni enables security teams to identify misconfigurations and excessive privileges before they’re exploited. This identity-aware insight across your entire SaaS ecosystem helps organizations maintain the rigorous verification and least-privilege access that zero trust demands, ensuring your security strategy protects not just network connections, but the applications and data that drive your business.